In-depth interpretation of why blockchain is inseparable from oracles?
Why is blockchain inseparable from
oracles? We should understand what an oracle !
The oracle writes external
information into the blockchain to complete the data exchange between the
blockchain and reality. Allowing smart contracts to map to the uncertain
external world is not only the only way for smart contracts to interact with
the outside world, but also the interface between the blockchain and the real
world.
01. Technically analyze the oracle
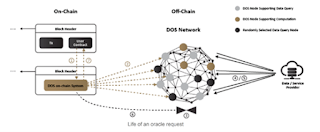
Structurally, oracles serve as an intermediate layer that securely connects blockchains to off-chain systems by connecting to data providers, web APIs, enterprise backends, cloud service providers, IoT devices, electronic signatures, payment systems, and A hub for various off-chain environments such as other blockchains, with the following key features:
·Wait for Response - Monitor the blockchain network and scan the network for off-chain data requests from users or smart contracts.
Fetch Data - Fetch data from one or more off-chain systems (e.g. off-chain APIs run by third-party web servers)
Formatting - converts data from APIs into a format readable by the blockchain, and converts on-chain data into a format compatible with external APIs, thereby breaking the communication barriers between on-chain and off-chain.
Verification – Provide cryptographic proofs for oracle services using a variety of tools such as data signatures, blockchain transaction signatures, TLS signatures, Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) proofs, and zero-knowledge proofs.
Calculations - perform operations on data, such as calculating the median based on data submitted by multiple oracles, or generating insurance quotes based on different types of data (such as personal risk profiles, market rates, and capital costs, etc.).
Broadcast - Send data and associated proofs to on-chain smart contracts by signing and broadcasting transactions on the blockchain.
Data output (optional) - Send data to off-chain systems when smart contracts are executed, such as sending payment instructions to traditional payment networks, or interacting with cyber-physical systems.
Therefore, in order to achieve the
above functions, the oracle system must run both on-chain and off-chain. The
role of the on-chain modules is to interact with the blockchain (waiting for
data responses), broadcast data, send proofs, obtain blockchain data, and
sometimes perform operations on the chain. The role of the off-chain module is
to process data requests, obtain off-chain data and convert formats, send
blockchain data to off-chain systems, and perform operations in a higher-level
oracle network.
Simply put, an oracle is a bridge
connecting the blockchain world and the real world, allowing the blockchain
world to obtain real-world data.
02. Understand the oracle from an
ecological perspective
In the early days of blockchain development, people were still at the stage of mining BTC, and what they pursued was only the competition of computing power. At that time, the ecology of the industry was extremely scarce. But with the influx of DeFi frenzy, the ecology of the blockchain has gradually developed, and the data interaction between the blockchain world and the real world is very important. Obviously, oracles have become an indispensable infrastructure in the crypto world, especially in the DeFi space.
For example, lending protocols rely
on price oracles to decide when to liquidate a user's loan. If a user's
collateral falls below a certain threshold, the account can be liquidated.
Derivatives platforms use oracles to calculate the value of crypto assets,
including options, futures, and synthetic assets. Additionally, index platforms
such as Set use oracles to retrieve the prices of index components.
Without oracles, the crypto world
would be chaotic without traffic lights.
However, when the external data
accessed is "fake" data, will it bring catastrophic damage to the
encrypted world? The answer is yes. Oracles need to be highly secure because
many things depend on them. If data entry is compromised, people lose money.
Such incidents of loss of platform assets due to fraudulent data on the chain
are not uncommon.
When we dig deeper into the
decentralized oracle network (DONs), we find that it is actually powering the
smart contract economy. A smart contract is a decentralized application with
coded logic (if event x occurs, execute action y), executed deterministically
on the blockchain network.
On the Ethereum mainnet, the
oracle, as a deployed smart contract and an off-chain component, can query the
information provided by the API, and then send messages to other contracts to
update contract data. But trusting only one data source is a very unreliable
way, usually multiple data sources. We can create it ourselves, or we can
directly use the services provided by the service provider. At the beginning,
centralized oracles did contribute a lot to the operation of smart contracts.
But over time, how to ensure the fairness and fairness of data sources has
become an urgent problem to be solved.
03.PlugChain: A Rookie of Decentralized Oracle
When the decentralized oracle was
born, these problems were easily solved. In particular, the decentralized
oracles with Chainlink and PlugChain as the mainstream have won the favor of
the market by relying on the "decentralized" oracle network protocol.
The difference is that Chainlink only focuses on the ecology of the only public
chain of Ethereum. The high-performance cross-chain PlugChain can combine the
ecology of 100 mainstream public chains.
In order to ensure the fairness and reliability of the data, PlugChain obtains data from multiple external sources, and eliminates the influence of a single malicious data through the aggregation of multiple data sources, so it is more reliable. Although decentralized oracles are relatively inefficient compared to centralized oracles, they can solve the problem of single-node failures, so they are less likely to bring security risks. Due to risk concerns, most DeFi applications prefer to run on decentralized oracles.
Of course, the PlugChain oracle network can not only transmit financial market data for DeFi applications, but also perform a series of secure off-chain calculations, such as verifiable random numbers and decentralized execution, to ultimately achieve dynamic NFTs and extremely high levels of automation. DApps. In addition, with the continuous development of cross-chain interoperability protocols, PlugChain will connect various rapidly developing blockchain ecosystems and L2 expansion schemes by virtue of its super cross-chain performance advantages, enabling them to interact securely.
Not only that, but PlugChain builds a secure DON by providing additional layers of security to ensure that DON operates efficiently, such as the ability to connect to high-quality data sources (providing accuracy and uptime guarantees), through cryptographic signatures Proof of data integrity (when data providers themselves run oracle nodes), data validation through multi-layer aggregation processes (mitigating downtime, outliers, and corrupted data), cryptoeconomic guarantees that incentivize correct operation (implicit incentives) and explicit collateral), as well as selectively provide data privacy.
In addition, PlugChain has expanded the Web3 technology stack to transmit off-chain data and services to promote smart contract innovation; to achieve cross-chain interoperability and ensure seamless connection of various blockchains. PlugChain's oracle architecture provides an entry for Web 2.0 backend systems to enter Web 3.0, provides an abstraction layer for traditional systems, and easily accesses any public and private chains. Ultimately, oracles will bring decentralized computing and cryptographic assurances to legacy systems and bridge the gap between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0.
04. Double layout of technology and ecology, adding Web3.0 public chain construction
In order to help develop the public chain ecology, PlugChain adopts a dual strategy layout of technical support and ecological support.
On the one hand, PlugChain relies on the advantages of its own public chain to establish a "fast lane", contract development platform access and blockchain platform construction, including contract sample templates, smart contract IDE, contract supporting SDK, integrated development environment, technical development documents, On-chain optimization guidance, smart contract development, node management settings, consensus mechanism design, monitoring and early warning system, Dapp on-chain deployment. Make it easier and faster for technology developers or ecological participants to join PlugChain. The "fast lane" is obviously a technical solution that provides more value to the developer ecosystem by reducing the time cost of project development.
On the other hand, PlugChain has established a PC ecological fund and recently launched the L Plug-Inside StarRise Plan to support the development of excellent ecological applications D. Facing the global high-quality ecology, PlugLabs (an agency under PlugChain) will provide support in four aspects according to the rating indicators: mainly including financial support, strategic support, advertising support, and traffic support! This will attract more high-quality ecosystems to join.
Whether it is the technical optimization of the PlugChain protocol, the improvement of blockchain scalability, or the support and subsidies provided in ecological construction through the StarRise Plan, these series of cost reduction measures can develop the PlugChain ecology into a public utility, benefiting Web3 of developers and DAPP teams.
Conclusion:
While DeFi is the clearest evidence
at the moment, it is more likely that the next major smart contract use case to
see mass adoption will be a direct result of developers accessing real-world
data on DONs on-chain. It can be seen that oracles have opened a new chapter in
the Web3 era and are ready to go beyond the existing ideas and functions. As a
public chain betting on DONs, can PlugChain create the future in the future?






Comments
Post a Comment