Interpretation of Oracle Ecology: In-depth evaluation of three mainstream projects: Chainlink, PlugChain, and ADAMoracle
Preface: The word Oracle originated from the character “Oracle” in ancient Greek mythology. According to legend, oracles can communicate with the gods on Mount Olympus, make predictions about the future, and convey the will of the gods to the people, so Oracle originally had the meaning of “prophet”. In computational complexity theory and computability theory, an oracle machine is an abstract computer used to study deterministic problems and can be viewed as a Turing machine with a black box (oracle) attached.
We know that the blockchain is a consensus-based network, and the inherent limitations of its consensus mechanism and deterministic virtual machine stipulate that smart contracts can only passively receive data. It is neither possible to actively obtain Internet data, nor to spontaneously call external network APIs, but most blockchain scenarios such as insurance and lending require active real-time acquisition of data in the real world, especially the Internet.
Therefore, oracles generally interact with the execution engine as an independent module of the blockchain or as a third-party service. The oracle is only responsible for the trusted acquisition of data and does not directly participate in the execution of transactions. In various oracle projects, most of them play the role of “middleware” in the physical world and the block world, so that smart contracts can actively obtain external data.
If the oracle belongs to a layer in the DeFi foundation, it connects the chain on and off the chain, and continuously transmits the data in the real world to the blockchain to ensure the normal execution of each smart contract. In order to allow more readers to understand the oracle project in more detail, this article deeply analyzes the mainstream well-known oracle projects in the market, so as to judge the advantages and disadvantages of them.
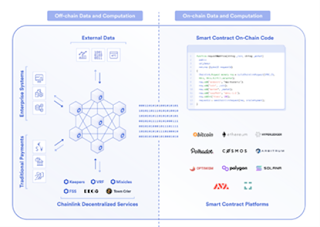
01. Chainlink: the leader of decentralized oracles
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle. It provides data for smart contracts through on-chain reputation contracts, node matching contracts, aggregation contracts, and a decentralised oracle network. Chainlink is the earliest project in the decentralized oracle, founded in December 2014. On May 30, 2019, Chainlink was officially launched on the Ethereum mainnet. With first-mover advantage and positive network effects, Chainlink is currently the most widely used oracle.
Chainlink uses multiple independent oracle nodes and multiple data sources to submit data, increasing the degree of decentralization of the network. Compared to other oracles that use free APIs, Chainlink uses paid APIs to fetch data, improving data quality.
In order to ensure the quality of data and prevent oracle nodes from making mistakes, Chainlink has designed a reputation system and a staking mechanism to score the performance of oracle nodes, give corresponding LINK rewards to nodes with good performance, and deduct the stakes of nodes with improper behavior. LINK.
Chainlink’s workflow can be divided into two parts, on-chain and off-chain. The on-chain module is responsible for connecting to the smart contracts of DApp developers and accepting data requests, while the off-chain module is responsible for monitoring requests and obtaining data from node operators.
Among them, the on-chain part of Chainlink includes three modules, namely reputation contract, order matching contract and aggregation contract, which are responsible for selecting oracles, reporting data and aggregating data. The off-chain part is a network of independent oracle nodes that listen for requests and obtain data from node operators.
It is worth mentioning that in order to ensure data privacy and tamper-proof modification, Chainlink adopts the privacy oracle solution — Deco to expand the data security function of the HTTP/TLS protocol (the mainstream method of Internet data transmission), thereby realizing advanced encryption technology. With zero-knowledge proof, data privacy and anti-tampering are guaranteed, and third parties, including the application using the data itself, cannot view the content of the data.
The settings of the three modules on the Chainlink chain allow developers to flexibly configure oracles that meet the requirements, which is beneficial to Chainlink’s business expansion. At the same time, in order to improve the privacy of the oracle machine, Chainlink developed Mixicles and acquired DECO technology. The verifiable random number Chainlink VRF launched by Chainlink expanded the use case of the oracle machine and accelerated the development of smart contracts in the fields of blockchain games and security. , which brings great value to smart contracts. Chainlink is the first oracle machine based on Ethereum, with a relatively complete ecosystem, strong business expansion capabilities, and continuous expansion of partners.
Chainlink’s reputation system and staking mechanism can motivate node operators to provide correct data, which improves the security of oracles and the accuracy of data. However, the staking mechanism has not yet been launched. Chainlink temporarily cooperates with trusted nodes. There is no penalty mechanism. Protected by node reputation and the opportunity cost of future revenue loss due to malicious offers.
Here is a summary of the following technical highlights about Chainlink:
As Chainlink, with its first-mover advantage and strong team, has become a leader in decentralized oracle machines, with 110,000+ currency holding addresses, and the number of cooperative projects is also in a leading position in the industry. But Chainlink is also controversial on some fronts.
Among them, Chainlink’s authentication service system has been controversial: nodes are naturally divided into tier1 (ordinary nodes) and tier2 (authentication nodes). As a result, the following potential risks will arise:
①The solution to the witch attack comes from the tier2 node. If the tier2 node is hijacked, the entire network can be hijacked;
② There is a conflict of interest between tier2 and tie1. If the tier2 node rebels, you can earn the tier1 node credit pledge Links directly by reporting an error to the tier1 node.
Obviously, its design architecture assumes an adjudication tier (tier2) to resolve disputes at the first tier. The adjudication layer itself has the potential for fraud based on interest. In essence, it still solves the security problem of decentralization in a centralized way (API3 proposes a DAO solution)
On the other hand, the growth rate of the number of Ethereum Dapps has slowed down significantly, and mainstream Dapps have been basically adapted by Chainlink. Since Chainlink currently supports the Ethereum network, its development scale has fallen into a bottleneck period. In addition, although the available/public WEB3 data requirements have been basically met, the Chainlink customized API service is still in its infancy, which makes the development of the Chainlink ecosystem slow.
02.PlugChain: The leader of aggregated cross-chain oracles
PlugChain is a Web3 public chain with high concurrency, low gas fee, and easy scalability as its core advantages. By building an aggregated cross-chain oracle protocol, it is committed to the application scenarios of high-performance information and data interaction. It is not difficult to see that PlugChain mainly focuses on two areas, cross-chain and decentralized oracles.
It can be said that the PlugChain based on Cosmos has a more compatible cross-chain framework and the team’s original cross-chain function, making it capable of 100 mainstream public chain services, which is a bit like the Polkadot intermediate chain and parallel chain. relation. In short, it combines the high efficiency and independent data interaction of Cosmos, and adopts the underlying functional components of Polkadot to achieve scalability between blockchains.
At the same time, the public chain collaboration of multi-chain aggregation enables a wider source of data on the PlugChain chain, which is not limited to the Ethereum network, but includes mainstream public chains such as BSC, Solana, Cosmos, Polkadot, Heco, and Polygon, which not only greatly improves the area The accuracy of the data on the blockchain also strengthens the decentralization of its oracle network.
The on-chain design of PlugChain is also relatively complete. The four modules perform their respective functions. The first is the proxy system for invoking user contracts; the second is the supervision system to ensure the authenticity of on-chain records and service quality; the third is the external chain Join the registration system of the verification node; the fourth is the payment system designed with a reasonable threshold. To ensure efficiency and scalability, PlugChain puts data computation off-chain, including verifiable computation outsourcing and distributed data feeds.
In addition, in order to realize data and information exchange between different chains, PlugChain adopts innovative heterogeneous sharding technology, which enables smooth interoperability in sharded blockchains. The so-called cross-chain composability refers to the Dapps and blockchains can communicate and interact with each other seamlessly. In short, PlugChain cross-chain composability allows smart contracts to be composed in a permissionless and seamless manner, even if they execute on different chains (shards) or run in different environments.
According to official news, PlugChainTPS is as high as 10K. In terms of data encryption, PlugChain adopts the threshold signature technology, which is a distributed multi-party signature protocol. In short, the threshold signature scheme is a method of replacing the digital signature scheme with an interactive protocol between multiple parties, which includes a key There are two parts to the generation and signature algorithm. A key generation protocol involves a set of n parties that interactively generate an m-out-of-n secret sharing of keys. Generally speaking, threshold signature has more advantages than multi-signature, and is more secure and professional.
To summarize the technical highlights of PlugChain:
Although PlugChain is the leader on the public chain of aggregated cross-chain oracles, there is still a gap compared with the development of Chainlink projects, which is mainly reflected in the sector of ecological cooperation. Although there are dozens of ecological projects deployed on PlugChain, there are no outstanding high-quality projects and lack of strong ecological endorsement. At the same time, in terms of cross-chain interaction, PlugChain has overlapping areas of competition with Comsos and Polkadot in cross-chain collaboration. Obviously, “cross-chain + decentralized oracle” is not only its advantage in many public chain fields, but also a challenge for its future development.
03.ADAMoracle: The leader of the wide-area node quotation oracle
ADAMoracle is the first decentralized oracle that supports wide-area node price feeds. It was the first to launch a wide-area node quotation system, which not only retains the traditional data source organization, but also adds a large number of diversified servers as computing nodes and storage nodes. Both the oracle machine and the data source realize a decentralized and complete oracle machine solution, support multi-chain operation, and can support various ecological application scenarios such as decentralized lending, asset synthesis, and prediction markets.
Similarly, ADAMoracle adopts the distributed oracle protocol, which includes modules such as how to become a data provider, data identification and verification, anti-attack algorithm, verifiable random function VRF, arbitration protocol, etc., through the complete decentralization of oracles and data sources. The overall solution of the oracle machine, in addition, ADAMoracle will also focus on the multi-chain oracle machine protocol, by realizing the cross-chain connection of mainstream public chains such as ETH, Polygon, Polkadot, BSC, etc., to open up the entire chain ecology and realize the borderless transmission of data and information.
This is similar to the PlugChain above. It can be said that ADAMoracle and PlugChain have the intersection of competition. Of course, there are differences between the two.
The innovation of ADAMoracle lies in the promotion of the domain node mechanism, which is the Oracle 3.0 system solution proposed by the ADAMoracle laboratory, which enables the oracle architecture to realize unbounded interstellar network computing. Its core function can connect thousands of diversified servers as price-feeding nodes for quotation, effectively constructing a safe and scalable oracle quotation system, which can not only ensure the accuracy of data transmission, but also better guarantee The decentralized nature and usable performance of the oracle network.
It is precisely because of the wide-area node price-feeding mechanism that the ADAMoracle oracle can filter out a certain scale of price-feeding nodes, which can effectively avoid the problem of a single data source, thus ensuring the accuracy of price-feeding data; at the same time, the more nodes there are, the more nodes conspire to do evil or The higher the cost of attacking the oracle system.
Summarize the technical highlights of ADAMoracle:
Although ADAMoracle was established in 2020, it has not made a substantial breakthrough in terms of its ecological development progress, and the ecology on the chain is relatively scarce. The token address of ADAMoracle’s token is 3834.
To sum up, ChainLink wins first-mover advantage and a large development team, as well as including mature Ethereum ecological scenarios, whether in terms of popularity, community popularity, or project popularity, ChainLink is still in the oracle machine track. head. But only limited to the application on the Ethereum chain, the future ecological boundary of ChainLink will be inferior to PlugChain and ADAMoracle. PlugChain and ADAMoracle highly overlap in business focus, but from the perspective of active addresses, community popularity, and project development, PlugChain is much more mature than ADAMoracle. Both have areas of expertise in their respective fields. The “wide-area node” practiced by ADAMoracle is also a big innovative idea.
All in all, in the short term, ChainLink is still the outlier, PlugChain and ADAMoracle are still catching up with the former. In the medium and long term, PlugChain and ADAMoracle have greater potential. After all, in the future multi-chain era, aggregated cross-chain + decentralized oracle network is more valuable!
Conclusion: The continuous development of the blockchain has led to its increasing demand for off-chain data. As a key way to realize trusted data on the chain, the oracle project is currently in its infancy, and there is a relatively simple trust guarantee mechanism and transaction costs. In the future, the oracle will focus more on functional work, improve the security, reliability and practicability of off-chain data on the chain, and serve blockchain applications.











Comments
Post a Comment